Configuring SSO and IdP in Flex
Twilio Flex integrates with your existing identity provider to authenticate users (agents, supervisors, or administrators) and enable single sign-on (SSO). You can integrate Flex with any identity provider that supports SAML 2.0, like Google, Active Directory, Okta, and others. This lets you use your primary corporate account as the identity provider for Flex.
- Identity provider (IdP): A trusted entity that lets you enable single sign-on to access other websites or services, like Flex, with a single login. Your users can keep using their corporate user identities without having to remember many passwords or having to retype passwords each time they access a different service connected to the same identity provider. An example identity provider is Okta.
- Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML): An open standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, in particular, between an identity provider and a service provider. SAML is an XML-based markup language for security assertions (statements that service providers use to make access-control decisions). Flex uses SAML version 2.0.
- Service provider (SP): An entity that's configured as an application on an identity provider to support single sign-on. In this context, Flex is the service provider.
Your Flex instance uses either enhanced or legacy SSO configuration, depending on when you created your Flex account. Both configuration types provide a reliable way to use your existing IdP to authenticate users with SSO.
Enhanced SSO configuration
- Provides a simplified setup experience and enhanced SSO based on the OAuth 2.0 authorization framework
- Applies to Flex accounts that are using Flex UI 2.5.x or later and are configuring SSO in Flex for the first time
- Migration available for existing Flex accounts that are using Flex UI 2.7.x or later
- Available for self-hosted Flex accounts that are using Flex UI 2.7.x or later
Legacy SSO configuration
-
Provides a traditional setup experience
-
Applies to Flex accounts that meet either (or both) of these conditions:
- Set up SSO in Flex before January 29, 2024
- Use Flex 2.4.x or earlier
Info
All Flex customers using the legacy SSO configuration need to migrate to the enhanced SSO configuration prior to March 31, 2026.
If you're not sure whether you have enhanced or legacy SSO configuration, compare your Single sign-on (SSO) page to the following screenshots:
| Enhanced SSO configuration | Legacy SSO configuration |
|---|---|
 or 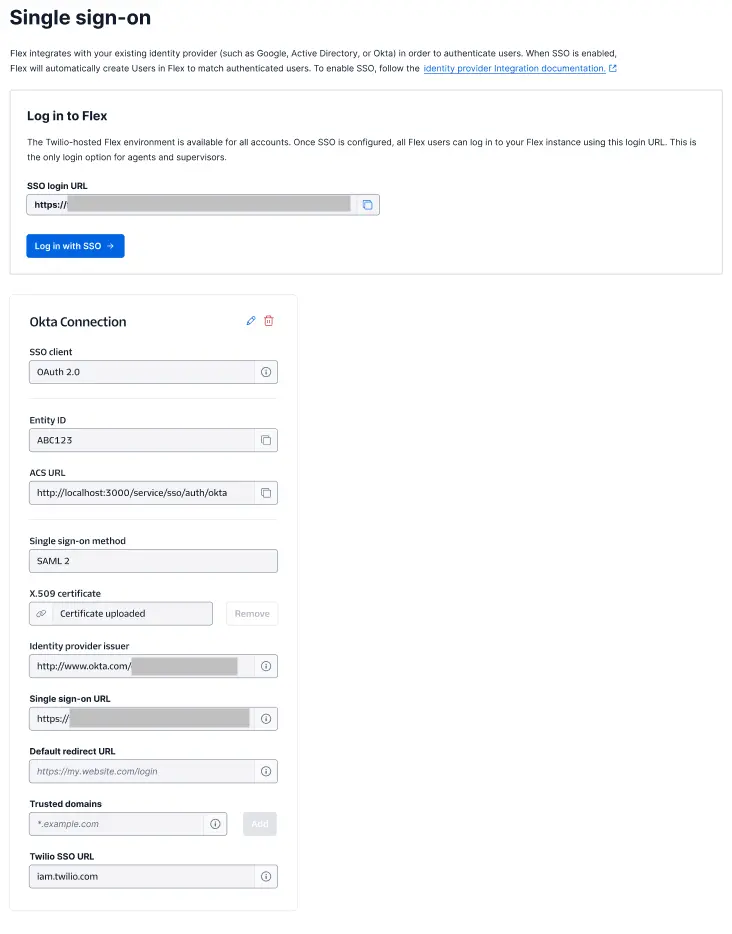 | 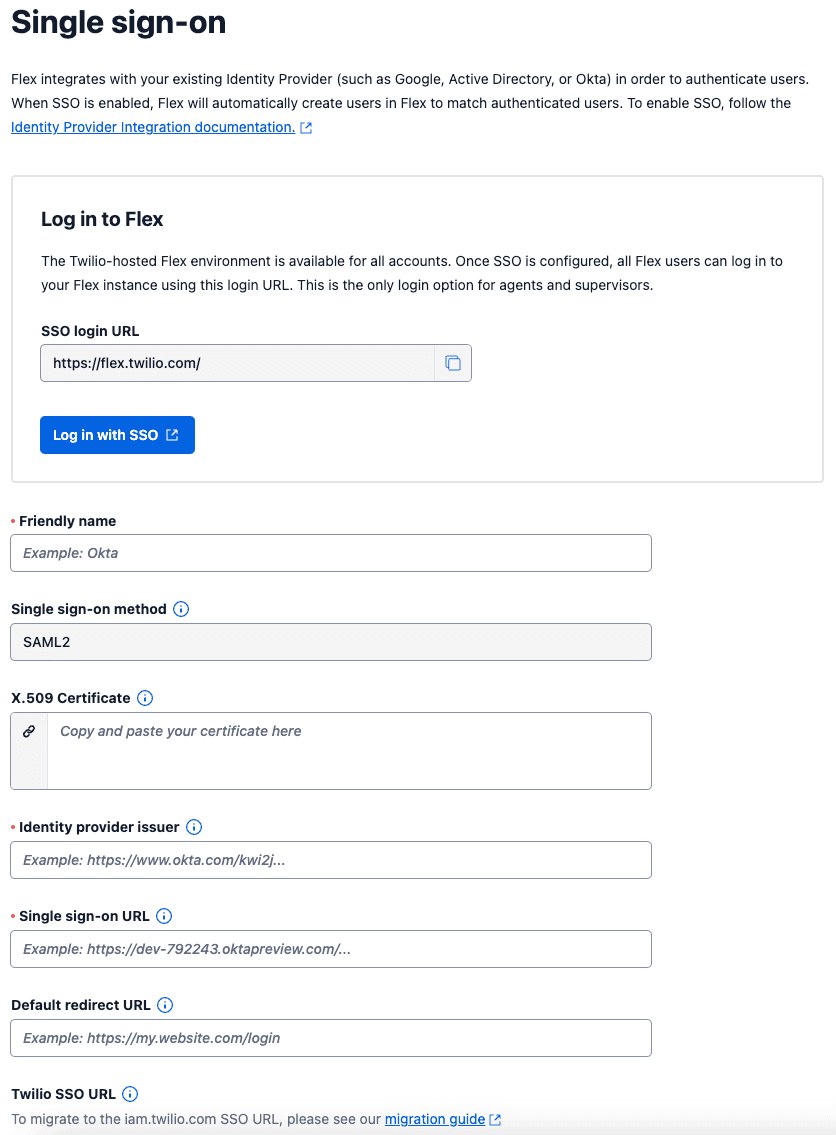 |
The steps to configure Flex as an application (service provider) within your identity provider will be different depending on which identity provider your organization uses. Below, you can find documentation required to set up Flex as a service provider in a few popular identity providers:
Your identity provider can provide any number of claims (key-value pairs) to Flex. These are mandatory:
- Unique ID or User ID
- List of User's roles
- Full name
The Unique ID should be provided in the request header, so it's likely you won't need to explicitly set it.
Flex includes the following roles:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
admin | Grants access to all of the pages in the UI. Admins can use the Flex Admin, Agent Desktop, Teams, Queue Stats, Dashboard, Analyze and also Questionnaires (Flex Insights features) and the Flex Dialpad (if enabled). |
supervisor | Grants access to Agent Desktop, Teams, Queue Stats and Dialpad (if enabled). |
agent | Grants access to Agent Desktop and Dialpad (if enabled). |
Flex stores the user data sent from the identity provider in the TaskRouter Worker attributes. This allows contact center developers to adapt the Flex UI using data about the logged-in user from your identity provider. The Worker attributes created for the logged-in user are updated on every successful SSO login, so any changes to user data made in your identity provider are also represented as Worker attributes.
Info
If you no longer want to pass a custom attribute from your IdP, update the attribute in your IdP by removing its value only, not the entire attribute.
If you remove the entire attribute, Flex won't update the TaskRouter Worker attribute after login. Because of this, you won't see any change to the attribute in Flex.
TaskRouter Worker attributes can be divided into these categories:
- Mandatory: The list of mandatory parameters required for Authentication and Authorization
- Flex-Agent: Parameters used by the Flex Agent Desktop
- Flex Insights: Recommended parameters if you use Flex Insights
By default, all attributes are transformed as strings to TaskRouter attributes except for the roles attribute, which defaults to stringarray (comma as separator). The roles attribute is a special attribute that accepts a comma-separated list of roles and doesn't require casting to stringarray.
You can state the attribute type in the attribute name using the following format: name.[type]
The following types are supported. Types are case-sensitive and must be written in lowercase, as shown:
stringintbooleanstringarrayintarraybooleanarray
| Attribute name | Type | Example value |
|---|---|---|
| name.string | String | Mary |
| skill.int | Integer | 1 |
| sales.boolean | Boolean | true |
| languages.stringarray | String Array | en,de,fr |
| skills.intarray | Integer Array | 1,2,3,4 |
If you incorrectly define the attribute type and value (for example, defining skill.int with a value of "a" or "1.23"), the following message appears in Flex: 400 Error invalid attribute format. No changes are made in TaskRouter for incorrect attribute definitions.
TaskRouter and the Twilio Voice SDK use contact_uri to dequeue a call. By default, the call is dequeued to the worker's contact_uri attribute using Twilio's JavaScript Voice Client (for example: client:userId). Flex automatically configures the contact_uri, so you don't need to set it within your identity provider. The specific identity value is escaped to only include alphanumeric and underscore characters.
The incoming call can also be dequeued to a SIP interface (for example: sip:recipient@example.com) or a phone number by setting contact_uri as a phone number (for example, +14151112222 - E.164 format). To dequeue to these identities, you need to set the contact_uri within your identity provider.
If you use Programmable Voice, when dequeuing the call to an international number, make sure the destination country is enabled in Twilio Console at Voice > Settings > Geo Permissions.
| Attribute name | Type | Value or example |
|---|---|---|
roles | Array[String] | agent, admin |
full_name | String | Bob Bobson |
email | String | john@example.com |
| Attribute | Type | Value or example |
|---|---|---|
image_url | String | http://www.someurl.com/bob_bobson.jpg |
| Attribute | Type | Value or example |
|---|---|---|
department | String | Sales |
email | String | mary.smith@example.com |
location | String | London |
manager | String | Adam Shepherd |
roles | Array[String] | wfo.team_leader |
phone | String | +15555555555 |
team_id | String | 1 |
team_name | String | Sales VIP |
team_name_in_hierarchy | String | London,Sales,VIP |
You can also define the TaskRouter capacity per channel with these attributes. For example, a new user added to Flex may be available for voice tasks and have a default chat capacity of 1. These can be modified using custom attributes:
| Attribute | Type | Value or example |
|---|---|---|
channel.voice.availability | Boolean | false |
channel.chat.capacity | Integer | 3 |
These special attributes can be formed for any of the TaskChannels that you have defined within your Flex TaskRouter Workspace.
To enable automated team assignments in Flex using SSO assertion, you must first set up and configure Teams in Flex as a Flex admin. Then, configure your IdP to include specific team designation attributes in the SAML assertion with the following mappings.
Attribute setup may differ slightly for each IdP. The following examples are specific to Okta, but should provide a general guide for supported IdPs. For specific setup instructions for your IdP, consult your IdP documentation.
- Name:
team_member - Name Format: Basic
- Value:
user.team_member(or the appropriate IdP expression for a single team name a user belongs to)
- Name:
team_owner - Name Format: Basic
- Value:
user.team_owner(or the appropriate IdP expression for a list of comma-separated team names the user owns)
| Attribute | Type | Value or example |
|---|---|---|
team_member | String | Team 1 |
team_owner | String | Team 1, Team 2, Team 3 |
The values asserted for team_member and team_owner for a user must match the names of existing teams exactly as they are in your application. This feature does not support automatic creation of new teams.
If your SAML assertion contains improperly formatted or non-existent team values, your application won't update the user's team membership or ownership. Consult your application's debug logs for detailed error messages about invalid team values and troubleshooting.
- Ensure that the team names configured in your IdP match the team names in your application. Pay attention to case sensitivity.
- Review your IdP configuration to confirm that the
user.team_memberexpression (or its equivalent) correctly retrieves the user's single primary team, and theuser.team_ownerexpression (or its equivalent) correctly retrieves the user's list of owned teams. - Monitor your application's debug logs after enabling this feature to identify and resolve any issues with team attribute assertions.
- If you provide multiple team values for the
team_memberattribute, the application logs an error and won't assign the user to any team. - If you provide multiple team values for the
team_ownerattribute, make sure to separate them with a comma (for example, Team 1, Team 2, Team 3). - In the SAML assertion:
- The
user.team_memberattribute automatically maps a user as a member to a team (for example, Team 1). If this attribute is empty or null during login, the user is mapped to the system-generated "default" team. - The
user.team_ownerattribute automatically maps a user as an owner to a team or multiple teams (for example, Team 1, Team 2, Team 3). If this attribute is empty or null, all team ownership assignments for the user are removed during login.
- The
Each user who logs in to Flex with a SAML identity provider automatically becomes a Flex user. To learn more, see Manage Flex UI users.
Warning
When enabling new Flex users with SSO, you will incur charges as soon as they log in. The pricing is noted on your Twilio contract if you're working with the Twilio sales team. To learn more, visit this Twilio Flex pricing article.
Flex also auto-provisions a TaskRouter Worker for this identity. TaskRouter is at the core of Flex and is required to enable intelligent skills-based routing of tasks to Agents or Supervisors.
Whenever a user logs in to Flex, all claims passed are checked and updated if necessary, using the identity provider as the source of truth. If you would like to update a specific Worker attribute directly then please do not configure it in the identity provider claims/attributes.
Yes, with the exception of Google Workspace single sign-on. The SSO Configuration in Twilio Console has an optional Default Redirect URL field. When provided, this allows IdP-initiated login to route into Flex. If your agents use Flex from flex.twilio.com, then provide the login link listed in your SSO Configuration. For example:
https://flex.twilio.com/dancing-owl-1234
Otherwise, you would use your own self-hosted Flex URL.
To enable SSO login for your self-hosted Flex deployment, you must first configure SSO in Flex Console. For your security, you must register all self-hosted URLs with Twilio. You can provide these trusted URLs in the Trusted URLs field when you configure SSO in Flex.
Use the following patterns when providing a trusted URL:
http://localhost:3000https://example.com/flex
Note that Flex's enhanced SSO configuration doesn't support wildcard domains (for example, *.example.com).
Warning
If you are using Flex's enhanced SSO configuration and have a custom domain, your Flex account must be running Flex UI 2.7.x or later.
Warning
If you have logged in through Twilio Console, avoid logging in using an SSO provider to prevent a secondary account created that will incur charges overtime. Likewise, logging in with your SSO provider and then logging into Twilio Console will grant you two separate profiles that will each be billed.
Yes, Twilio Console users (except those that only have the Billing role within Console) have access to Flex. They can launch Flex from within the Twilio Console, and they log in with the Flex Administrator role. Support users log in with the Read-only Administrator role. (For more details, see Manage Flex UI users.) We recommend this approach for your admins and developers when your application is under development.
Note that Flex creates different users depending on the login method. For example, a user with the same email address will create two Flex personas if they log in using two alternate methods, for instance, if they log in with SSO and then again directly using the Console using Twilio credentials.
You can trigger the Login with Twilio option in two ways:
- By selecting Launch Flex from Twilio Console. This is available on the Flex Overview page.
- By selecting Login with Twilio on the default Flex login view.

Option 1 will always log in to Flex at flex.twilio.com. If you are self-hosting the Flex UI, this won't load your private destination.
Option 2 is available for self-hosted locations and for local development, such as logging into localhost when developing plugins.
Info
As mentioned in How do I configure SSO to work with a self-hosted Flex configuration?, you must register your destination as a Trusted URL. Otherwise, neither your SSO login or the Login with Twilio option will work.
If you use a self-hosted Flex deployment, you must configure SSO before you can register a trusted URL, which is required to log in using Console. To work around this, you can set up SSO using placeholder information for the IdP. Once SSO is enabled, you can register a trusted URL to redirect users to your self-hosted Flex instance.
Note: localhost domains do not require this workaround.
The login view only loads if you haven't provided the sso attribute within your application configuration. If the sso attribute is provided (or you are using your flex.twilio.com Login Link), then you will bypass the login view and immediately trigger SSO login.
After logging out, users will always be sent to the Flex login view. You can't use the afterLogout action to redirect to another page.
You can configure the SessionNotOnOrAfter attribute within your identity provider to ensure a maximum TTL (time-to-live) for an authenticated session. After the configured time, a user will be forced to authenticate within their identity provider in order to extend their session with connected applications.
We don't recommend using this attribute alongside Twilio Flex. When a user is logged in to Flex UI, Flex regularly refreshes the user's Flex Token (the authenticated token that grants access to the UI). If the identity provider session expiration comes before the Flex Token's expected refresh period, Flex won't be able to refresh the user's session. Any active communications may be prematurely closed once the user's authentication expires, and the user will need to refresh the Flex application and re-authenticate through their identity provider.
If you choose to use SessionNotOnOrAfter, you must use a value greater than 1 hour (the default TTL of the user's authenticated Flex Token). We recommend setting this value above the shift time for an agent (for example, 8-10 hours). Otherwise the agent may be logged out of Flex unexpectedly. Even if you use a long TTL, users may still be impacted if they first log in to Flex mid-way through their active authenticated session.
To help troubleshoot, install the SAML Tracer Chrome Extension. This tool will parse SAML responses for review during troubleshooting.
The first time you try to log in to Flex through your newly configured SSO connection, you might encounter the following error message: "This XML file does not appear to have any style information associated with it. The document tree is shown below."
This error appears from your IdP when the single sign-on URL isn't configured correctly. Your IdP provides your single sign-on URL, and you enter it on the Flex SSO configuration page. First, confirm that you entered the URL correctly in Flex. If so, search your IdP documentation to ensure you have located the correct URL for this field.
Each claim that you define in your identity provider should map to an attribute on the provisioned TaskRouter Worker. If an attribute doesn't appear, this may be the result of a namespace that's being applied to your claims. You can identify this if the attribute name in the SAML is a URL schema. For example:
1<Attribute Name="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/email">2<AttributeValue>jdoe@example.com</AttributeValue>3</Attribute>
However, Flex will correctly interpret the following attribute:
1<Attribute Name="roles">2<AttributeValue>wfo.full_access</AttributeValue>3<AttributeValue>admin</AttributeValue>4</Attribute>
This error typically occurs when the Claim Transformation was not properly set. The SAML response will show something like:
1</ds:X509Certificate>2</ds:X509Data>3</KeyInfo>4</ds:Signature>5<samlp:Status>6<samlp:StatusCode Value="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:status:Requester">7<samlp:StatusCode Value="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:status:InvalidNameIDPolicy" />8</samlp:StatusCode>9</samlp:Status>10</samlp:Response>
Note the InvalidNameIDPolicy value in the Requester StatusCode.
If the SAML response looks valid, check that the identity provider Issuer field in Flex Console Single-sign on page is correct.
This response occurs when the roles aren't passed to the claims. Check your claims configuration and review the roles attribute.