Integrate the Mindful platform With Flex
This implementation guide will step you through the integration between Flex and Mindful platform. With this integration, you can respect your customers' time and give them control by letting them choose when they'll receive a call. Whether it's two minutes or two hours, your customers will appreciate spending less time waiting on hold.
Mindful offers two types of callback, Customer-First or Agent-First. These callback experience options are selectable per queue. A Customer-First callback calls the customer back first and ensures they are ready for their callback. If they are not ready, Mindful handles disconnects or voicemail and will attempt to contact them again (if configured). If they are ready, the callback will connect the customer to an agent. Agent-First callback calls the agent first, and once connected, the customer is called.
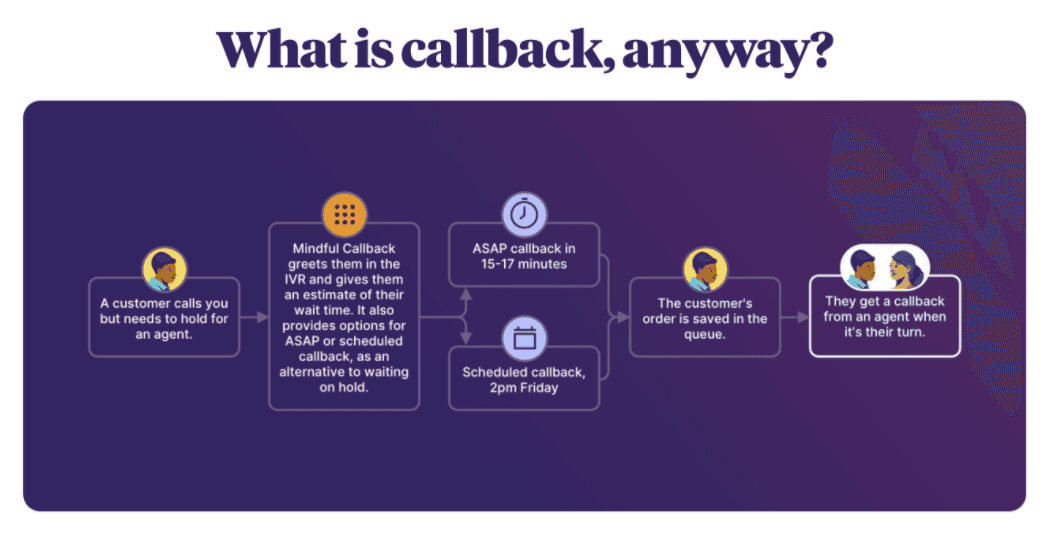
When your queues are full and your agents are swamped, new inbound calls are going to have longer hold times. This can lead to abandoned calls, poor customer experience, increased service costs (as you deal with repeat attempts by a customer), and fewer opportunities to help and engage with your customers.
One of the best ways to reduce hold time is to give callers an option to skip it altogether. With Mindful, you can offer customers the option to call them back at a more convenient time. This works great for contact centers that have peaks and valleys in their contact volume; you take the contact volume that arrives during your peak volume time and you handle it when your staff isn't as busy.
Implementation guide disclaimer
This guide has two primary sections:
- Setting up the connection with Mindful
- Demonstrating two example call flows that incorporate callbacks.
The example call flows are a guide, and you should adapt them to fit your desired customer experience. Similarly, the sample code provided is a guide and doesn't incorporate standard techniques like error handling. These should be refined based on your needs before integrating into a live environment.
Here is a high-level overview of the connectivity with Mindful:
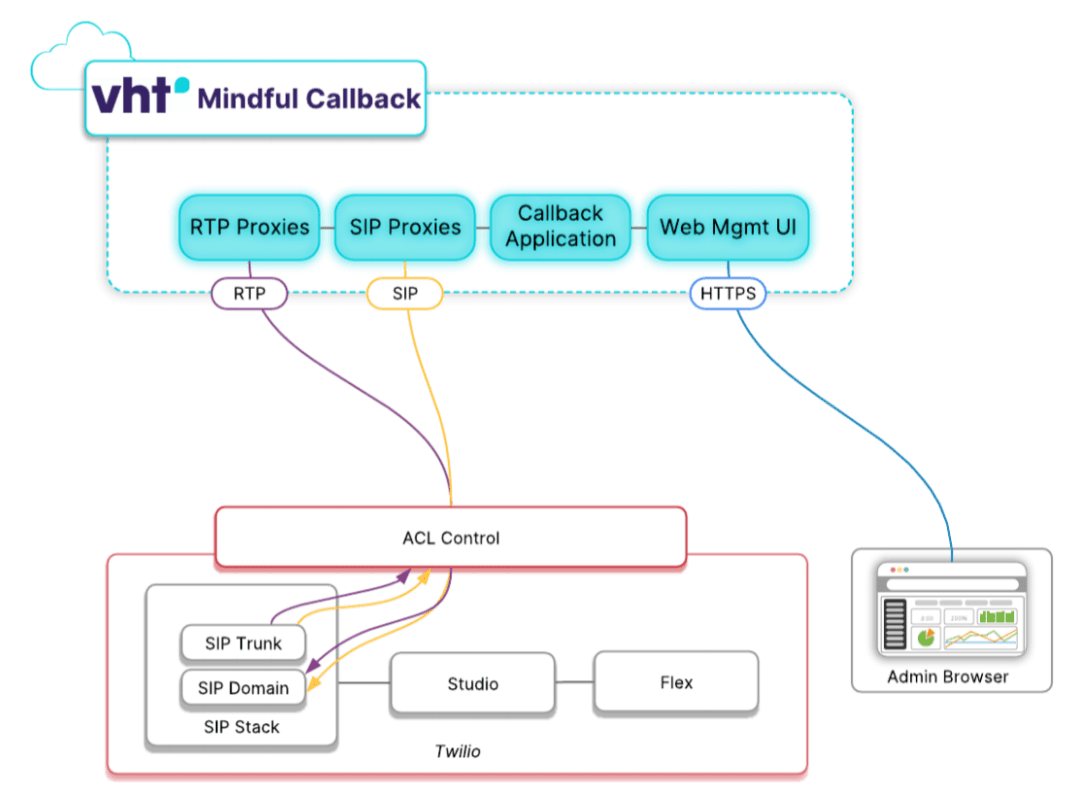
You will need to set up a SIP Domain and SIP Trunk which will be used to transfer calls to Mindful, as well as a dedicated phone number, which will be used for the Callbacks.
Follow these steps to establish connectivity with Mindful:
In Twilio Console, go to Active Phone Numbers.
This solution relies on two phone numbers, one for incoming calls from your customers and one for incoming calls from Mindful. These numbers will route to separate Studio Flows which will be configured later on in this document. Don't forget to update the routing of these phone numbers after you have completed the Studio Flows.
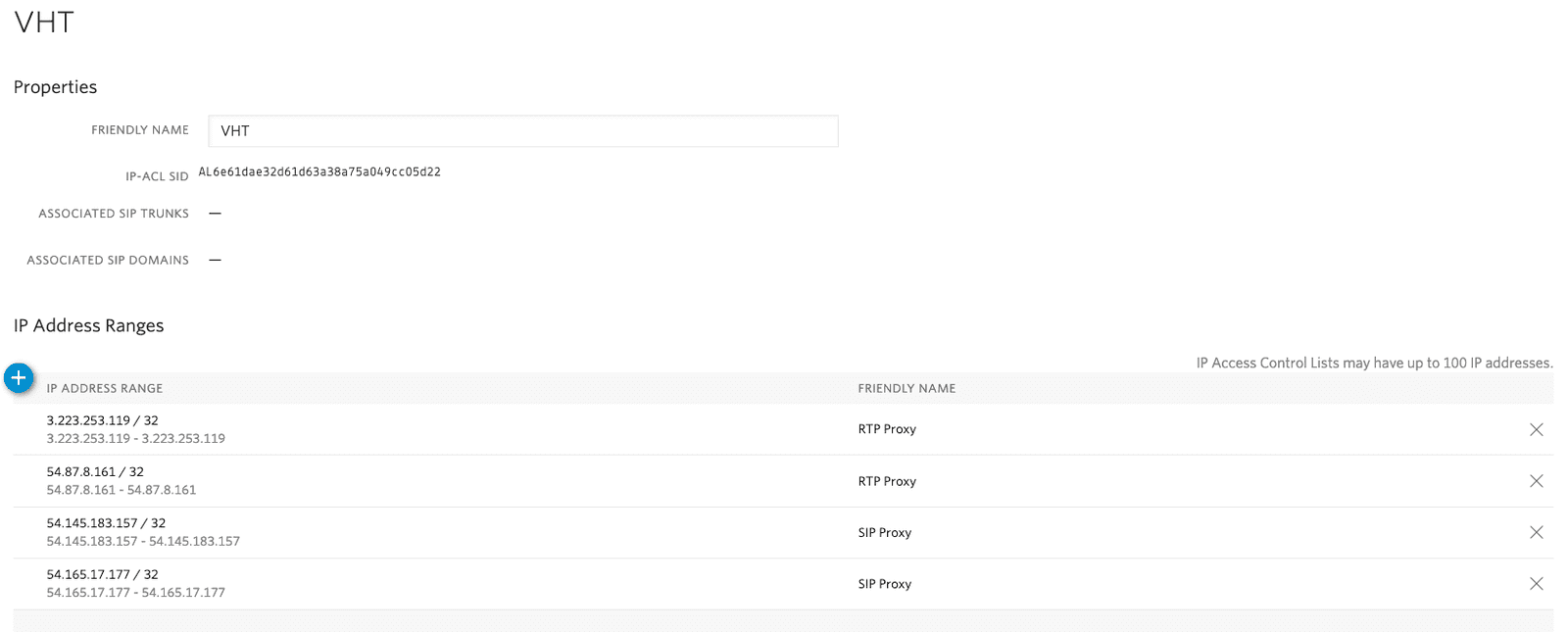
- In Twilio Console, go to IP / CIDR Access Control List
- Create a new ACL with the following addresses:
54.165.17.177/32 - VHT SIP Proxy 54.145.183.157/32 - VHT SIP Proxy 54.87.8.161/32 - VHT RTP Proxy 3.223.253.119/32 - VHT RTP Proxy
- In Twilio Console, go to Programmable SIP Domains
- Create a new SIP Domain
Hint: Use the IP access control list defined in step 1
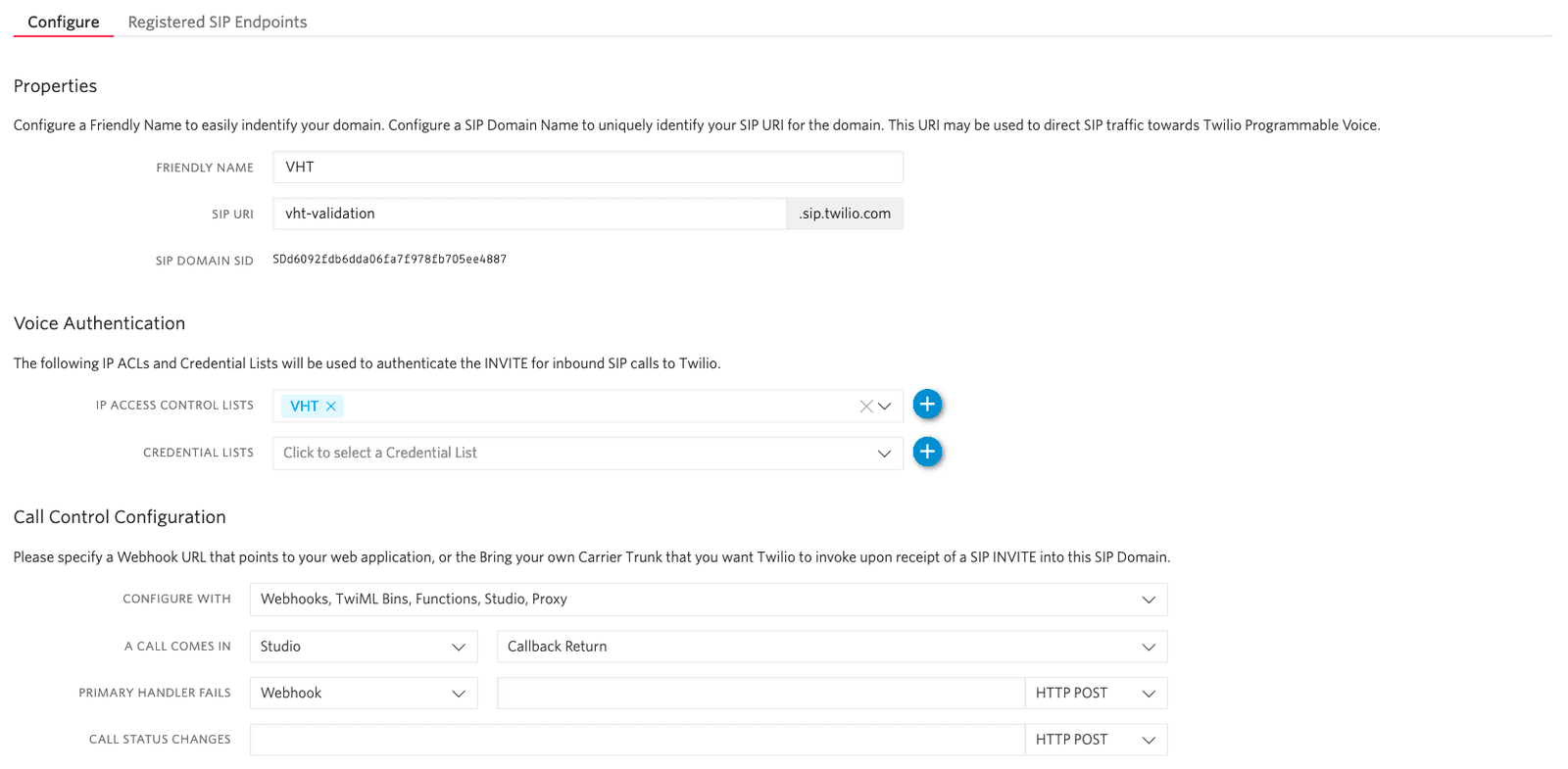
In this example, incoming calls to this SIP domain route to a Studio flow, which is configured later in this document. You can also use other options, such as a Function that returns TwiML.
- In Mindful, go to Call Targets, Add New CT; or click here.
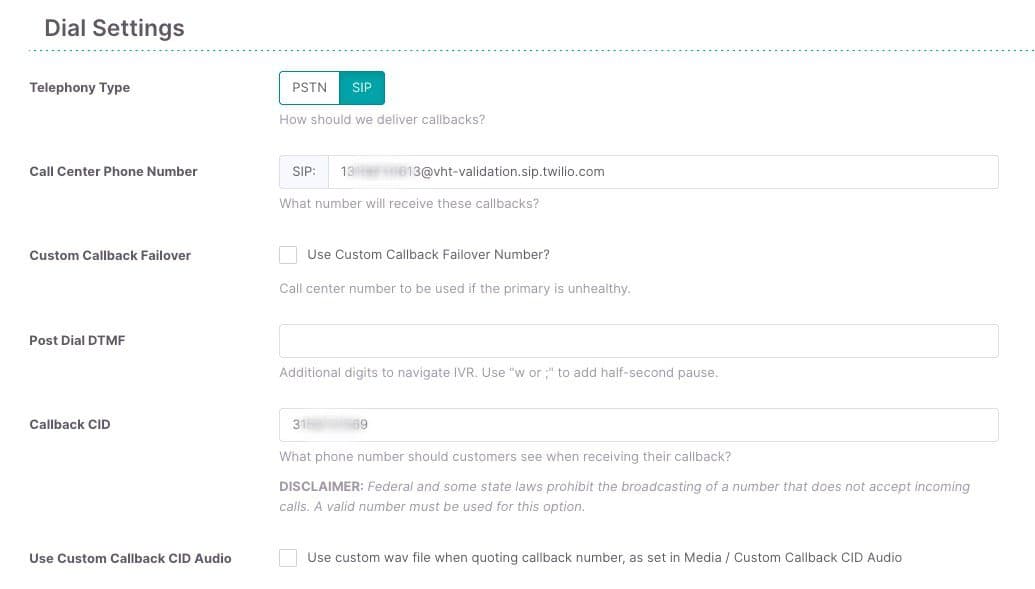
- Change the Telephony Type to SIP.
- For the Call Center Phone Number, enter the phone number which you use for the return calls from Mindful.
- For Callback CID, enter the Twilio phone numbers callers are calling. This will be used as the caller ID when returning the callback.
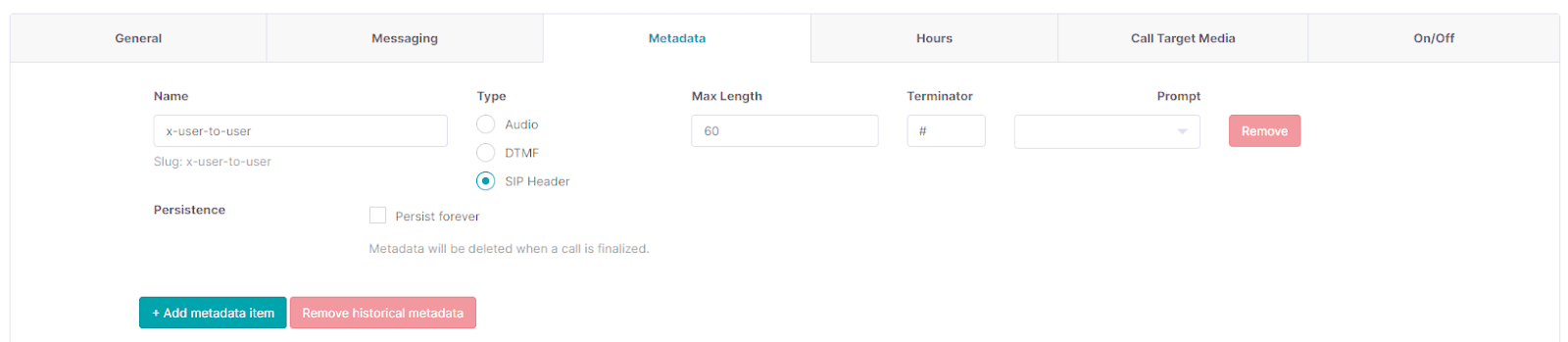
- Go to the Metadata tab.
- Add a metadata item called x-user-to-user with the following settings:
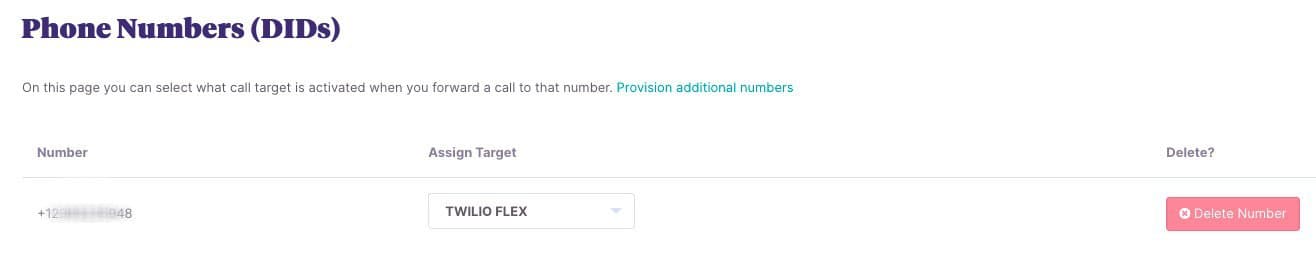
- Go to Phone Numbers.
- Provision a new phone number and assign it to the Call Target configured in step 4.
Before sending an incoming call to a TaskRouter task queue, call a Function that uses the TaskRouter Statistics API to determine the Estimated Wait Time. If this is above a threshold, you can offer the caller the option of a callback instead of sending the call to a queue.
Best practices for offering callbacks
- When quoting the estimated wait time prior to offering a callback, it is a best practice to set an upper limit for the amount of time that can be quoted. For example, if the wait time exceeds 10 minutes, you might choose to say "...more than 10 minutes from now" rather than quoting an exact time.
- We recommend setting a minimum offer threshold based on the current estimated wait time to ensure that callback offers are not made when wait times are very low. You may also wish to check agent availability prior to offering a callback.
The TaskRouter Statistics API doesn't provide a true Estimated Wait Time, but there are multiple ways to calculate it. This example uses the AvgTaskAcceptanceTime value that is available in TaskRouter for the previous five minutes.
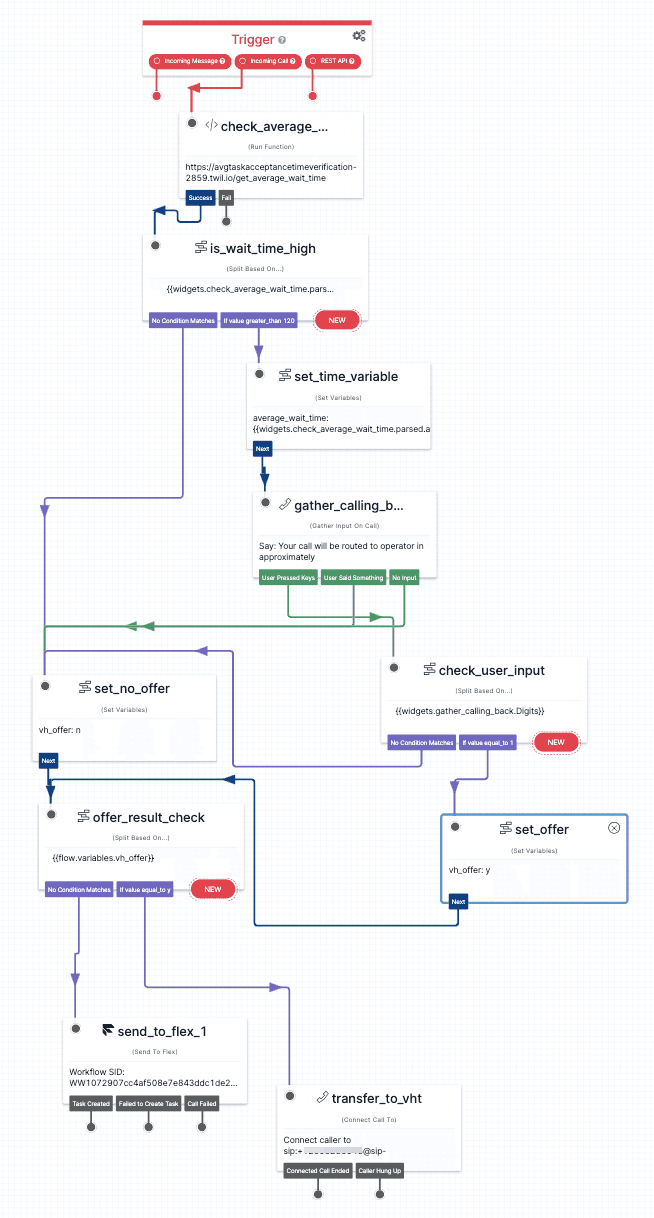
In diagram above, the Estimated Wait Time is obtained by using Studio's Run Function widget (in the diagram called check_average_wait_time) and invoking a Function with following code:
1/**2* Function to read avgTaskAcceptanceTime statistics from TaskRouter's cumulative statistics.3* https://www.twilio.com/docs/taskrouter/api/taskqueue-statistics#taskqueue-cumulative-statistics4*5* It returns JSON object with following fields:6* - avgTaskAcceptanceTime - number of seconds7*8*9* Expected variables from context:10* - Queue_Estimated_Wait_Time - initial value of 0, used by script to cache value of average task acceptance time11* - Queue_Estimated_Wait_Time_Last_Updated - initial value of 0, used by script to cache timestamp of last update of12* - Queue_Update_Interval - average time update interval in milliseconds, initial value of 6000013* - Workspace_SID14* - Task_Queue_SID15* - Service_SID16* - Environment_SID17* - VAR_QEWTLU_SID - SID of variable Queue_Estimated_Wait_Time_Last_Updated18* - VAR_QEWT_SID - SID of variable Queue_Estimated_Wait_Time19*20* Following twilio-cli calls are useful for setting up environment variables for this script:21*22* twilio api:taskrouter:v1:workspaces:list23*24* twilio api:taskrouter:v1:workspaces:task-queues:list \25* --workspace-sid WSXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX26*27* twilio api:serverless:v1:services:list28*29* twilio api:serverless:v1:services:environments:list \30* --service-sid ZSXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX31*32* twilio api:serverless:v1:services:environments:variables:list \33* --service-sid ZSXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX \34* --environment-sid ZEXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX35*/3637exports.handler = function (context, event, callback) {3839const response = new Twilio.Response();40response.appendHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');41response.appendHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'OPTIONS POST');42response.appendHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json');43response.appendHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'Content-Type');4445get_wait_time(context, event, callback).then(value => {46response.setBody({47'avgTaskAcceptanceTime': value48});49return callback(null, response);50})5152}5354async function get_wait_time(context, event, callback) {55const client = context.getTwilioClient();5657let current_timestamp = new Date().getTime();5859if ((current_timestamp - context.Queue_Estimated_Wait_Time_Last_Updated) > context.Queue_Update_Interval) {6061let average_task_acceptance_time = await get_queue_cumulative_statistics(client, context.Workspace_SID, context.Task_Queue_SID, 'avgTaskAcceptanceTime');6263context.Queue_Estimated_Wait_Time = parseInt(average_task_acceptance_time);6465await client.serverless.services(context.Service_SID)66.environments(context.Environment_SID)67.variables(context.VAR_QEWT_SID)68.update({69key: 'Queue_Estimated_Wait_Time',70value: average_task_acceptance_time71});72await client.serverless.services(context.Service_SID)73.environments(context.Environment_SID)74.variables(context.VAR_QEWTLU_SID)75.update({76key: 'Queue_Estimated_Wait_Time_Last_Updated',77value: current_timestamp78});7980}8182return context.Queue_Estimated_Wait_Time;83}8485async function get_queue_cumulative_statistics(twilio_client, workspace_sid, task_queue_sid, stat_name) {86return twilio_client.taskrouter.workspaces(workspace_sid)87.taskQueues(task_queue_sid)88.cumulativeStatistics()89.fetch()90.then(stats => {91return (stats[stat_name]);92});93}
Info
If you receive the following error during execution, go to service dependencies and update the twilio library's version (e.g., to *) and redeploy.
1UnhandledPromiseRejectionWarning: Unhandled promise rejection: TypeError:2Cannot read property 'services' of undefined at get_wait_time3(/var/task/handlers/ZN016166710a27ef5a1f9efa721c2809e2.js:40:33) at4processTicksAndRejections (internal/process/task_queues.js:97:5)
If the Estimated Wait is greater than 120 seconds, the call is transferred to Mindful via the SIP trunk. Otherwise, the call is sent to Flex via a TaskRouter task queue.
The toolstep named transfer_to_vht defines the SIP endpoint to which Flex transfers the call. This is the phone number that you set up above in step 5, in the following format: sip:+1xxxxxxxxxx@sip-callback.mindful.cx:5566?x-user-to-user={{trigger.call.From}}
Flex also sends Mindful the caller's phone number through the user-to-user SIP Header.
In this example, the incoming call reaches the TaskRouter task queue in the Studio Flow.
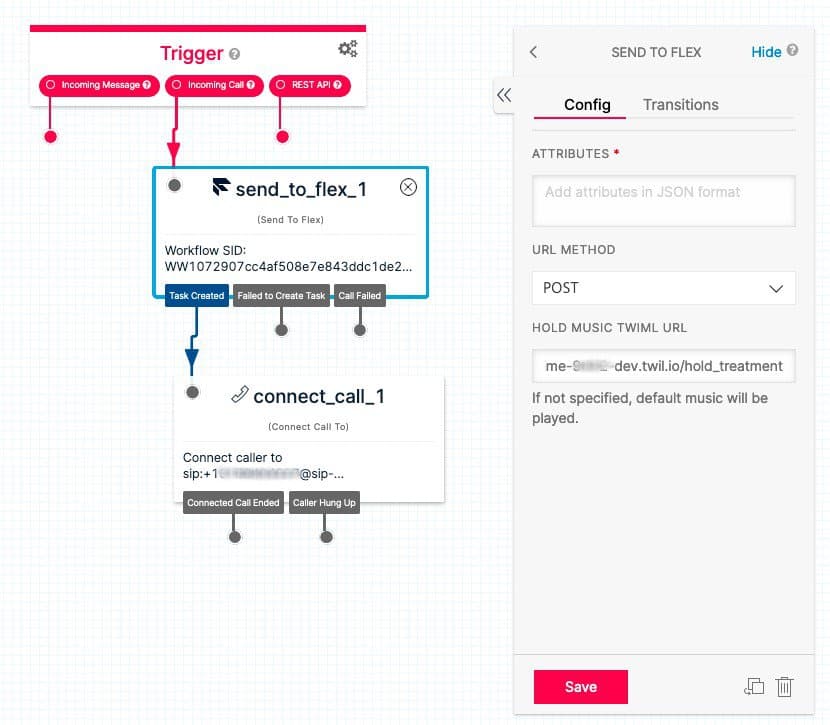
The average wait time check is performed in the widget Send to Flex (send_to_flex1 in the diagram above) by using the Hold Music TwiML URL parameter. Instead of pointing to actual Hold Music TwiML, you can point to a custom Function called hold_treatment(), which in turn calls another custom function transfer_to_vht().
Info
Careful planning and consideration should be given to taking a caller out of a task queue to receive a callback. The take-rate is lower when users are offered callbacks in-queue instead of before they enter the queue.
Code for hold_treatment:
1/**2* This function expects the same environment variables as the wait_time.js3*4* Expected variables from context:5* - Queue_Estimated_Wait_Time - initial value of 0, used by script to cache value of average task acceptance time6* - Queue_Estimated_Wait_Time_Last_Updated - initial value of 0, used by script to cache timestamp of last update of7* Queue_Estimated_Wait_Time8* - Queue_Update_Interval - average time update interval in milliseconds, initial value of 600009* - Workspace_SID10* - Task_Queue_SID11* - Service_SID12* - Environment_SID13* - VAR_QEWTLU_SID - SID of variable Queue_Estimated_Wait_Time_Last_Updated14* - VAR_QEWT_SID - SID of variable Queue_Estimated_Wait_Time15*/16exports.handler = function(context, event, callback) {17let twiml = new Twilio.twiml.VoiceResponse();1819get_wait_time(context).then(avg_wait_time => {20let action_url = "https://" + context.DOMAIN_NAME + '/' + 'transfer_to_vht';21if (avg_wait_time > 120) {22twiml.gather({action: action_url})23.say(`Your call will be routed to an agent in approximately ${avg_wait_time / 60} minutes. Press 1 if you want to be called back`);24}25return callback(null, twiml);26});2728};
Code for transfer_to_vht:
1exports.handler = function(context, event, callback) {2let response = new Twilio.twiml.VoiceResponse();34let gathered_digits = 0;5if (event['Digits']) {6gathered_digits = parseInt(event['Digits']);7}8if (gathered_digits && (gathered_digits === 1)) {9// leave Flex queue and continue with next node connected to Task completed10response.leave();11}1213return callback(null, response);1415};
When the Estimated Wait Time exceeds the threshold, in this case, 120 seconds, the function returns <Leave> TwiML which returns control back to Studio and continues with the next widget.
On the Task Created condition, Studio will use the Connect Call To widget and redirect to Mindful.
The last step of this Implementation Guide is to route the return calls from Mindful straight to Flex, but with a higher priority. This should be used as a followup for either of the two scenarios above.
You can do this with the following Studio Flow:
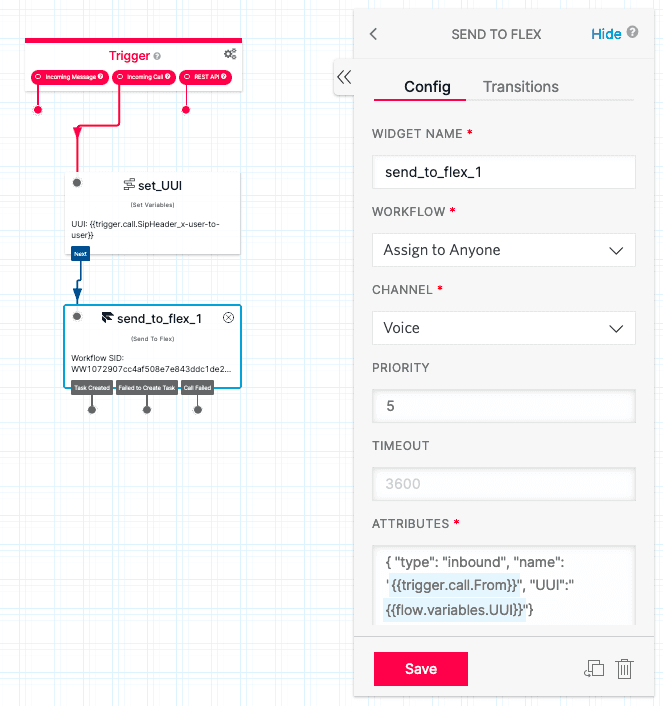
This Flow will grab the Sip Header x-user-to-user and set that as an attribute to the TaskRouter task. It also changes the Priority from a default value of 0 to 5, to give these incoming calls a higher priority. Depending on your organization's TaskRouter setup, you may need to change this value to one that is appropriately ranked.
Once you've connected all of your Studio Flows to the appropriate phone numbers, your callback solution should be ready to go. Well done - your customers will thank you for saving them from those long hold times!