Inbound SIP REFER to Twilio
Info
If you are looking for Outbound SIP Refer, use the TwiML verb <Refer>
Call transfer enables you to move an active call from one endpoint to another. Twilio's Programmable Voice SIP calls now support "blind" call transfers using SIP REFER. This means you're now able to request an active SIP call to be transferred by sending Twilio a SIP REFER message from your SIP communications infrastructure. Twilio can then serve as the pivot-point and handle the call redirect, allowing you to free up resources in your IP communications infrastructure that are no longer needed.
The call transfers can be invoked on both inbound and outbound SIP calls. For example, on an inbound SIP call from your SIP phone to a Twilio SIP Domain, you may want to transfer the caller to a different agent by pressing the "Transfer" button on your phone. Your SIP phone will send a REFER containing the contact information of the new agent, instructing Twilio to initiate a transfer. Twilio will accept the REFER, and can initiate the transfer to bridge the initial caller with the new agent. Similarly, you can initiate a transfer using a REFER towards Twilio on an outbound SIP call from Twilio to your SIP endpoint.
A SIP REFER from your SIP endpoint will trigger a webhook to your application containing call data, including the contents of the Refer-To header in the ReferTransferTarget parameter. On the initial call, you set the referUrl attribute in your <Dial> verb to define the application URL which will receive these webhook requests. As long as one leg of your call is a SIP connection, Twilio will honor the SIP REFER message that your SIP device is sending. You could also send contextual information in your SIP REFER as a UUI header or Custom header by including it as part of the Refer-To header; the contents will be passed in the webhook as part of the ReferTransferTarget parameter.
Info
REFER works for SIP calls created using the <Dial> verb using one of the following nouns:
<Sip><Number><Client>
REFER does not currently support <Conference> and <Queue> nouns.
Info
The maximum supported length of the Refer-To header in the SIP REFER you send to Twilio is 256 characters.
Ensure that referUrl is present in the initial call's <Dial> Verb attribute.
| Attributes | Allowed Values | Default Values |
|---|---|---|
| referUrl | Any URL | None |
| referMethod | GET, POST | POST |
The REFER details, including the ReferTransferTarget contact information, is passed on in the resulting Webhook to the referUrl. Your application can then handle the webhook however it likes, you are allowed to use any of the Programmable Voice features like <Dial>, <Say>, <Play>, <Gather>, <Enqueue>, <Sim>, etc.
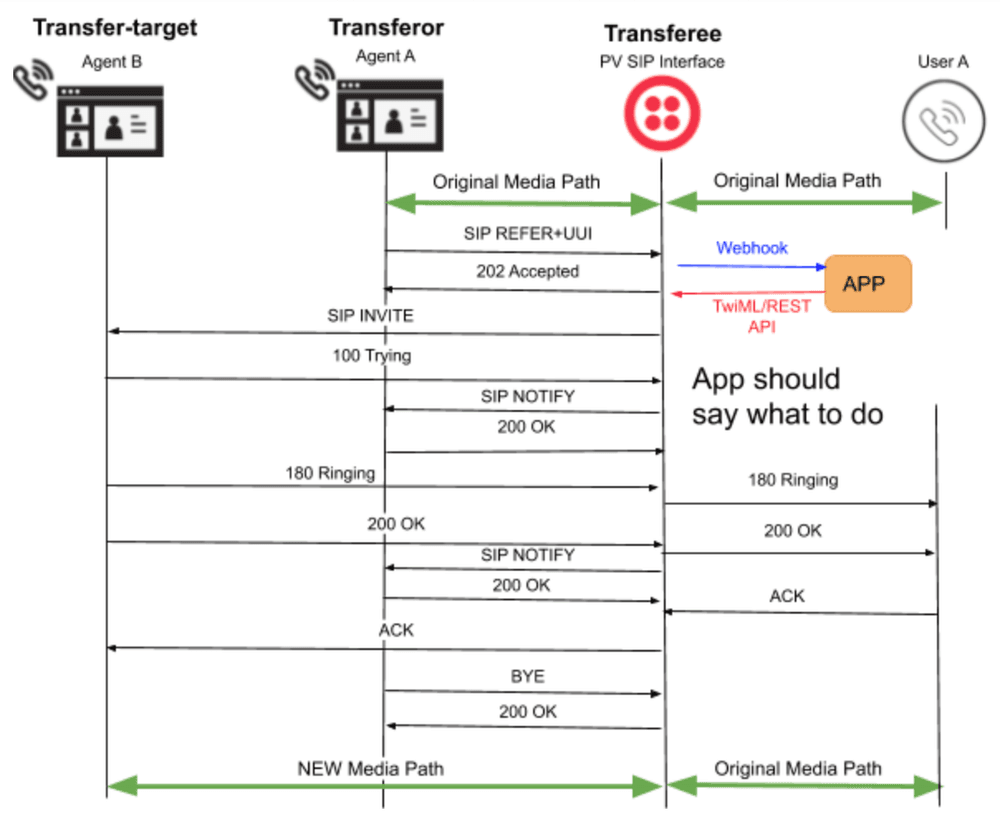
Here is an example call flow.
-
UserA called a bank and connected with Bank AgentA's SIP phone.
- It is at this step where the <Dial> verb will need to contain the
referUrlattribute.
- It is at this step where the <Dial> verb will need to contain the
-
They finished their initial conversation and now UserA wants to connect to AgentB in another department, so AgentA sends the SIP
REFERto Twilio containing AgentB's contact information in theRefer-Toheader. -
Twilio handles the
REFERand sends the information in a webhook to the customer's application, which establishes a call to AgentB's SIP phone using a TwiML <Dial> verb. Twilio then bridges UserA's call with the connected SIP call to AgentB.
Info
An example of the TwiML that your referUrl application could return is as follows:
1<Response>2<Dial>3<Sip>sip:AGENTB@YOURDOMAIN.sip.us1.twilio.com</Sip>4</Dial>5</Response>
Where Agent B's SIP Address was retrieved from the ReferTransferTarget parameter in the SIP REFER.
Note: A referUrl is not necessary in this leg of the call.
1const VoiceResponse = require("twilio").twiml.VoiceResponse;23const response = new VoiceResponse();4const dial = response.dial({5referUrl: "https://example.com/handler",6});7dial.sip(8"sip:AgentA@xyz.sip.us1.twilio.com?User-to-User=123456789%3Bencoding%3Dhex&X-Name=Agent%2C+A"9);1011console.log(response.toString());
Output
1<Response>2<Dial referUrl="https://example.com/handler">3<Sip>sip:AgentA@xyz.sip.us1.twilio.com?User-to-User=123456789%3Bencoding%3Dhex&X-Name=Agent%2C+A</Sip>4</Dial>5</Response>
The above example does not set the answerOnBridge attribute in the <Dial> verb; i.e., that attribute uses the default value of false. Therefore, right after the Webhook is fetched Twilio will immediately sends the SIP NOTIFY, and disconnects the "Transferor" call leg (AgentA in the above call flow). If the Transfer-Target (AgentB in the above call flow) does not answer the call, or if the call or Application fetch fails, UserA's call will be disconnected unless your application is written to be able to handle the failure case.
1const VoiceResponse = require('twilio').twiml.VoiceResponse;23const response = new VoiceResponse();4const dial = response.dial({5answerOnBridge: true,6referUrl: 'https://example.com/handler'7});8dial.sip('sip:AgentA@xyz.sip.us1.twilio.com?User-to-User=123456789%3Bencoding%3Dhex&X-Name=Agent%2C+A');910console.log(response.toString());
Output
1<Response>2<Dial answerOnBridge="true" referUrl="https://example.com/handler">3<Sip>sip:AgentA@xyz.sip.us1.twilio.com?User-to-User=123456789%3Bencoding%3Dhex&X-Name=Agent%2C+A</Sip>4</Dial>5</Response>
The above example sets the answerOnBridge attribute to true in the <Dial> verb. Therefore, Twilio will not disconnect the "Transferor" call leg (AgentA in the above call flow) until after the Transfer-Target (AgentB in the above call flow) answers the call. If the Transfer-Target (AgentB in the above call flow) does not answer the call, or if the call or Application fetch fails, UserA's call will stay connected with AgentA.
In this example, we will follow the call flow explained above.
- Initial call - UserA calls AgentA. They are connected and actively in conversation.
- Refer - UserA wants to connect to another department in the bank. AgentA presses the transfer button and passes on the contact information.
- Final call - UserA is now connected to AgentB. The initial call is torn down.
| Scenarios | Initial call status answerOnBridge is true | Initial call status answerOnBridge is false or not set |
|---|---|---|
referUrl webhook is executed | Initial call is still connected | Initial call is disconnected |
| AgentB answers the call | Initial call will now get disconnected | Initial call got disconnected right after the referUrl webhook is executed, see above |
| AgentB does not answer the call | Initial call can be re-established. So UserA will be connected to AgentA again | Initial call got disconnected right after the referUrl webhook is executed. Re-establishing the initial call will not be possible |
referUrl is not reachable | Initial call can be re-established. So UserA will be connected to AgentA again | Initial call got disconnected right after the referUrl Webhook is executed. Re-establishing the initial call will not be possible |
referUrl attribute is not present in the <Dial> Verb | Twilio will generate an alert and initial call will be re-established. So UserA will be connected to AgentA again | Twilio will generate an alert and initial call will be re-established. So UserA will be connected to AgentA again |