How TaskRouter Works
Twilio TaskRouter is a system for distributing tasks such as phone calls, leads, support tickets, and other work items to the people and processes that can best handle them. Example applications for TaskRouter include:
- Distributing calls to call center agents. TaskRouter supports common features required in call center environments, such as skills-based routing and task prioritization.
- Prioritizing and assigning CRM cases to agents in order to make sure they're handled within service level. Custom rules can vary assignment based on time spent in queue and case content.
- Distributing leads to sales teams. TaskRouter's business rules provide control over prioritization so that teams are always working on the most important opportunity.
Want to get started quickly? Dive into the TaskRouter QuickStart.
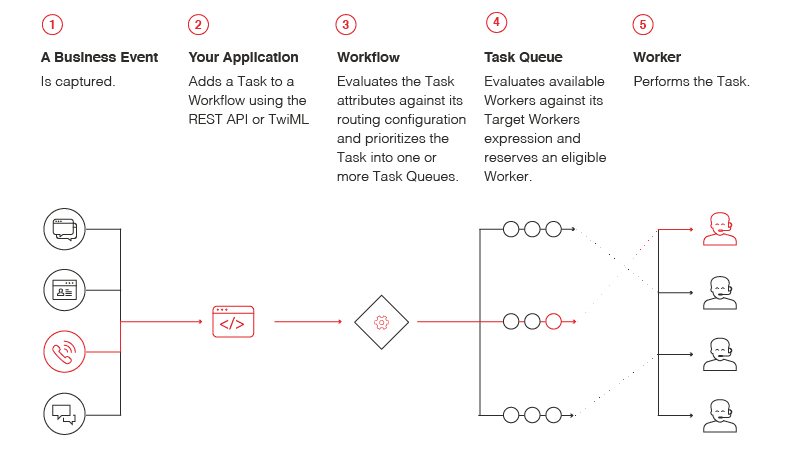
A TaskRouter Workspace is composed of many entities that work together to enable a Task to match a Worker, someone who can take action on the pending Task. This is accomplished through a few steps:
- Creating a Task and passing it through a Workflow
- Evaluating a Task's attributes to identify how it should route
- Routing the Task into a TaskQueue composed of Workers
- Finding the subset of Workers who have attributes that make them a match for the Task
- Pairing the Task with a Worker through a Reservation
- Completing the Reservation once the work represented by the Task is done
Each step taken by TaskRouter emits Events which log all activity within the Workspace. These events can be used for reporting, or applications can subscribe to the events and trigger new actions.
The JavaScript SDK is the recommended method for interacting with TaskRouter. Most TaskRouter applications display Task information to agents in a front-end application. The SDK simplifies the process for listening to TaskRouter events and eliminates roundtrips to a backend application attempting to coordinate all TaskRouter activity.
A typical TaskRouter application will:
- Generate tasks through the REST API or TwiML
- Have agents logged into an Agent UI, each subscribed to events through the JS SDK
- Listen to events, like
reservation.created, to identify when a Worker has been matched to a Task - Complete the reserved Task through the SDK
In addition, applications can listen to Event Callbacks. These JSON web requests cover a wider range of events, and they can be used by back-end services to track information across an entire Workspace. These callbacks can be useful to generate realtime reporting dashboards by aggregating event information, like worker.activity.update and task.completed events.
TaskRouter is a powerful tool when combined with other Twilio products. For Tasks that represent voice calls, TaskRouter can tie the lifecycle of a call to the lifecycle of a Task. This is particularly useful for automatically adding the assigned Worker as a participant in a Conference with an inbound caller.
Queueing Twilio Calls provides more detail on how to setup these integrations.
A TaskRouter Workspace is multitasking by default. A Worker's capacity (defined by their WorkerChannels) determines if they can handle three simultaneous chats, a voice call and a chat, or only one voice call.
TaskRouter uses a Worker's capacity and their Activity to determine if they are available for a new Task. When TaskRouter is assigning a Task through a Workflow, it will:
- Find Workers who match a Task based on attributes defined in a Workflow
- Ensure selected Workers are in an
Availableactivity and have remaining capacity on the Task's channel - Distribute Reservations to the Workers who have been longest without an assignment, or who match a custom-defined sort
-
Setup: Create Workers with the appropriate attributes, a TaskQueue associated with the Workers, and a Workflow to control Task assignment and escalation rules.
-
Put all Workers in
Offline -
Create a new Task. The Task will sit in queue until a matching Worker is available.
-
Update a Worker to an
Availableactivity -
TaskRouter identifies the available Worker and creates a Reservation pairing the Worker with the Task. The Worker's capacity is taken by the pending Reservation.
-
TaskRouter emits a
reservation.createdevent to the JS SDK and as an Event Callback. -
Respond to the JS event to accept the Reservation.
- If the Task was a voice call created through
<Enqueue>, accept with aconferenceinstruction to automatically bridge the Worker into a Conference with the inbound caller.
- If the Task was a voice call created through
-
Complete the Task from the JS SDK once the Worker is finished. The Worker's capacity is released. The process repeats as new Tasks are created.
-
Update the Worker to
Offlineto end their shift.
Want to get started quickly? Dive into the TaskRouter QuickStart.
- Learn more about the lifecycle of a Task, using Workflows to manage assignment, or blueprints for designing a contact center.
- Use the REST API to create TaskRouter resources and learn about each entity.
- Use the JavaScript SDK to manage an agent's connection to their Tasks in the browser.