What is Call Routing?
Call routing refers to the procedure of sending voice calls to a specific queue based on predetermined criteria. A call routing system is also known as an automatic call distributor (ACD).
Since traditional models of customer service were based on phone support as the primary method of contact between customers and companies, the procedure of sending calls to the right agent became known as call routing. However, modern agents interact with customers through a variety of channels. The call center has evolved into the contact center.
Today, SMS messages, chat and messaging requests, support tickets, leads, or even machine data are routed based on pre-set attributes, such as skills required by the agent, time zone or language preferences, and priority of the task. This process is often referred to as attribute-based routing, which matches tasks to the people or processes that can best handle them.
When there's a queue of customers waiting on the line, most businesses agree: getting those customers connected to the right agent as quickly as possible is a high priority.
Call routing allows businesses to connect their customers to the right agent faster. Attribute-based routing assesses the needs and context of each caller and connects them to the most qualified agent available with the skills to address those needs. Priority-based routing lets businesses elevate the most important callers to the front of the queue.
Intelligent call routing (or task routing) isn't just beneficial for customers. It also increases agent productivity by ensuring that agents are working on the right task at the right time, instead of prioritizing less urgent tasks or working on tasks that they aren't suited for.
Call routing helps customers not only have their needs met quickly, but also have an overall better experience. By anticipating customer needs and automating actions where possible, call routing creates a more personalized and efficient customer experience—which has a direct impact on a business's bottom line.
Consumer research shows that 67% of customers will give more business to a company as a result of positive communication experiences. But after a poor communication experience, 38% of customers will switch to a competitor or cancel orders or services, 66% will tell a friend about their experience, and 41% will stop doing business with the company altogether.
In cases where human agents aren't necessary, call routing enables virtual assistants and interactive voice response (IVR) systems to provide instant help. In fact, Gartner predicts that customer preferences for independence and self-service automation will likely rise to 85% by 2020.
An IVR system with custom-built menus can expedite incoming calls, accurately route callers, or even schedule a callback, reducing both the cost and the time to resolution.
Because customers prefer self-help features over waiting on hold for human contact, implementing an IVR system makes good business sense. This is especially true since IVR-handled calls can cost 100 times less than those involving a live agent. Equipped with intelligent call routing, IVR systems can reduce operating costs while increasing customer satisfaction.
Twilio TaskRouter is an example of an attribute-based routing API, for calls as well as other channels of communication, such as SMS messages, or interactions from any other system such as a CRM. TaskRouter dynamically routes incoming tasks to the agents that can best handle them based on applied attributes, such as skills required by the agent and priority of the task.
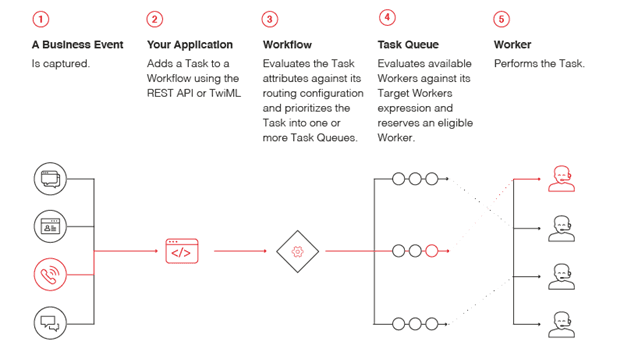
Twilio chose TaskRouter as the routing engine for the contact center application platform Twilio Flex, which can handle thousands of agents in one instance, because of its powerful ability to dynamically filter workers, optimize and prioritize tasks, and strategize for workers taking tasks on multiple channels concurrently. TaskRouter is at the very heart of every Twilio contact center deployment.